Liquid Oral Preparations Pharmaceutics-2023-24
Table of Contents
Liquid oral preparations
Introduction— Pharmaceutical liquid preparation is intended for the internal and external use in the form of liquid consistency of the one or more than one chemical (API)/solute in the specific solvents (water, alcohol) either in the homogenous mixture or heterogenous mixture.
Advantages
- It having the more advantage for the patient compliance, whose are not able to swallow the solid dosages form.
- It is useful for unconscious patient, child, old age people.
- Preparation and processing are cheap and easy than the solid dosages form.
- For the consuming no extra vehicle or required.
- Its bioavailability and absorption rate are high than solid dosages form.
Disadvantages
- Aseptic technique is very important because it is very sensitive towards microbial growth than the solid dosages form.
- Dosages adjustment is the major problem in the liquid preparation.
- Undesirable taste and smell.
- Handling and transportation are not easy.
Classification of liquid oral preparation.
- Monophasic liquid dosage form.
- Internal use— Solution, syrup, mixtures, linctus’s, elixirs.
- External use— Mouth gargle, mouth wash, nasal drops, ear drops
- Biphasic liquid dosages form.
- Internal use— Suspension.
- External use— Emulsion.
Simple Solution
Introduction—Pharmaceutical Solutions are homogeneous mixtures of two or more than two components. By homogenous mixture we mean that its composition and properties are uniform throughout the mixture.
- Generally, the component that is present in the largest quantity is known as solvent. Solvent determines the physical state in which solution exists.
- One or more components present in the solution other than solvent are called solutes. Dilute solutions, prepared from rapidly dissolving materials, are simply prepared by charging the solute to the solvent and agitating until the solution is homogeneous.
- When more concentrated solutions are being made, or when the solute is slowly dissolving, it may be advantageous to employ heat. Many types of pharmaceutical solution available in the market—
- Prednisolone oral solution.
- Theophylline oral solution.
- Cloxacillin oral solution.
- Ranitidine solution
Syrups
Definition— They are silent, Viscous, Concentrated solution of sucrose or other sugar substitute in water or any other suitable vehicles with or without flavouring agents and medicinal substances. Syrups containing flavouring agents but not medicinal substances are called non medicated or flavoured vehicles (syrups).
Components of syrup.
- The sugar, usually sucrose, or sugar substitute used to provide sweetness and viscosity.
- Antimicrobial preservatives
- Flavourings agents.
Classification of syrup
- Simple Syrup
- Medicated Syrup
- Flavoured Syrup
- Simple Syrup— Simple syrup is concentrated solution of sucrose/sugar in purified water. The concentration of sugar is 66.7 % W/W as per I.P or approx 85% W/V as per U.S.P.
Preparation of simple syrup
According to B.P simple syrup is prepared by adding 1Kg of refined sugar to 500ml of boiling distilled water and heating until it is dissolved and adding Boling distilled water until the weight of the whole is 1.5kg. The specific gravity of the Syrup should be 1.33
- Medicated Syrup— They are aqueous solution Containing sugar and at least one water soluble active ingredient. The sugar concentration should be between 65-67%.
Preparation of medicated syrup.
- API and additives, in a suitable solvent system pour into the mixing vessel. Mixed until the solution is formed.
- Heat might be applied to enhance dissolution.
- Then filtration is done. Which ensure the clarity of the solution.
- Then solution is passes into the manufacturing vessels. Here recycling process occurs.
- Finally, solution passes into the homogenizer to the filter press.
- Then solution is obtained.
Examples— Cough syrup, paracetamol syrup etc.
- Flavoured Syrup— It is typically consisting of a simple syrup that is sugar with naturally occurring or artificial (Synthesized) flavour that are also dissolved in them.
Ex- Ginger syrup, Lemon syrup etc.
Elixirs
Definition — Elixirs are sweetened, clear, hydro-alcoholic (water and alcohol) liquids for oral administration. Typically, alcohol and water are used as solvents when the drug will not dissolve in water alone. In addition to active drug, they usually contain flavouring and colouring agents to improve patient acceptance.
- The main ingredients of elixirs are ethanol and water but glycerine, sorbitol, propylene glycol, flavouring agent, sugar and preservatives may be incorporated to the preparation.
- The medicated elixirs usually contain very potent drugs such as antibiotics and sedatives.
- The bitter and nauseous test of certain drug can be mask by adding flavouring / sweetening agent.
Classification of elixirs.
- Non-medicated elixirs— These employed as vehicles for medicinal substances. Ex— Elixir of glycerine, aromatic elixirs.
- Medicated elixirs— These contain ingredients giving them therapeutic value. Ex— chlorpheniramine elixirs, paracetamol elixirs.
Preparation of elixirs.
- Dissolved the alcoholic-soluble and water-soluble components in the alcohol and water respectively.
- Then both the component is mix together.
- Finally, mixture is makeup with the suitable vehicles and then filter it.
Storage— Since elixirs contain alcohol and usually some volatile oils which is contaminate of presence of air and light therefore, they should be store in tightly closed, light resistance container and in a cool place.
Emulsions
Definition— Emulsion is defined as biphasic liquid dosage form containing a mixture of oil and water and addition of emulsifying agent or emulgent to product emulsion. Commonly emulsifier used as-Ex- Acacia, gelatin, soaps etc.
- An emulsion is a dispersion in which the dispersed phase is composed of small globules of a liquid distributed throughout a vehicle in which it is immiscible. It is also called as the heterogeneous system.
- Some of the emulsion present naturally like- milk, rubber latex, crude oil etc. some of having the medicinal properties like liquid paraffin is used as purgative and laxative. Most of the emulsion used as the vehicles for administering the drugs.
- Major advantage- it having the high surface area so, spread easily on the body and show their effect. It masks the unpleasant taste and smell of the drugs.
Classification of Emulsion.
- Based on mode of dispersion
- W/O (Water in oil)— Water is an internal phase and oil is in continuous phase OR Dispersed phase is water and dispersion medium are oil. Example, cod liver oil consists of particles of water dispersed in oil.
- O/W (Oil in water)— Oil is an internal phase and water is in continuous phase OR Dispersed phase is oil and dispersion medium are water. This type of emulsions is meant for both internal and external use.
- External— Benzyl benzoate emulsion, gamma benzene hexachloride.
- Internal— Vitamin A in corn oil, liquid paraffin in water.
- Based on the particle size
- Coarse emulsion/macro emulsion— This emulsion is generally formed if the aqueous phase constitutes more than 45 % of the total weight and a hydrophilic emulsifier is used. It is also known as conventional emulsions or macroemulsions having the particle size of diameter >200 nm range and kinetically stable.
- Micro emulsion— Microemulsion is a thermodynamically stable fluid that differs from kinetically stable emulsions, which will separate into oil and water over time. The particle size of microemulsions ranges from about 10–300 nm it appears as clear or translucent solutions.
- Fine emulsion— Fine emulsion have a milky appearance and the globules size range from 0.25 to 25 µm (micrometer).
Formulation of emulsion.
Following ingredients are included in the formulation of emulsion.
- Oil phase— This phase medicament or vehicle is made up of fixed oil mineral oil, volatile oil or also resin type that is used for preparation of emulsion.
- Aqueous phase— Due to increased risk of microbial contamination freshly boiled and cooled purified water are used.
- Antioxidant— It prevents the oil form getting oxidation hence It enhance the stability of the oil phase in the emulsion.
- Flavouring agent— It enhances the palatability of the final product pineapple, orange, chocolate, and mint flavours are commonly used.
- Colouring Agent— It is used for identifying the preparation and enhancing its aesthetic appearance. Erythrosine tartrazine etc, colours approved by the food Drug and cosmetic act are used as Colouring Agent.
Common Preparation method of emulsion.
- Collects all the requirement ingredients and groups on the basis of their solubility in the aqueous and oil phases.
- Dissolve the oil soluble ingredients and emulsifier in the oil.
- If necessary, heat the mixture to approximately 5 to 100 C over the melting point of the highest melting ingredients or to a maximum temperature of 70 to 800
- Dissolve the water-soluble ingredients (except acid and salts) in sufficient quantity of water.
- Heat the aqueous phase to a temperature, which in 3 to 50 C higher than that of oil.
- Add the aqueous phase to the oil phase with suitable agitation.
- If acids or salts are employed, dissolve them in water and add the solution to the cold emulsion.
- Transfer the preparation into a measurer and adjust the final volume with the water/dispersion medium.
- Pack the emulsion in a narrow-mouthed container and label it.
NOTE— Small scale preparation is done by the wet gum (English) method, and dry gum (continental) method.
Tests for the emulsion.
- Dilution test— This test is depended on the fact that when a dispersion medium is added to an emulsion, no phase separation occurs. When water is added to O/W emulsion, it is freely miscible with the emulsion and no phase separation occurs. Similarly, addition of oil in W/O emulsion shows miscibility.
- Conductivity test— when the water is continuous phase then it conducts the electricity. But in case, oil in continuous phase then it not conducts the electricity.
- Creaming test— it is based on the densities of the oil and aqueous. W/O normally cream downward as oil is usually less dense than water. O/W emulsions normally cream upwards.
Suspensions
Introduction— A course dispersion in which insoluble solid are suspended in a liquid medium with the help of the suspending agent known as pharmaceutical suspension.
Advantages.
- Improve chemical stability.
- Higher rate of bioavailability.
- Drug can be dispensed as suspension.
Disadvantages.
- Physical unstable.
- Uniform drug delivery difficult to achieve.
- Stability is poor.
Classification of suspension.
- Based on the proportion of the solute/solid.
- Dilute suspension—Dilute suspension may contain about 2 to 10% w/v solids. Examples- cortisone acetate and prednisolone acetate.
- Concentrate suspension— Concentrated suspension contain solids as high as 50% w/v. Example- Zinc oxide for external use and procaine penicillin G as an injection.
- Based on the nature and appearance of the solid distribution.
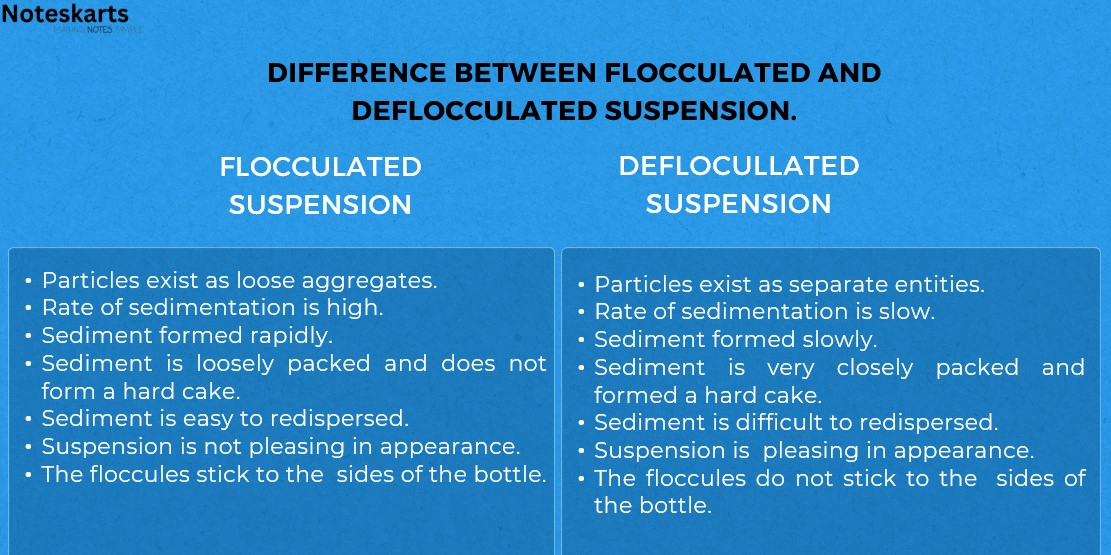
- Flocculated suspension— In this system, particles aggregate themselves by chemical bridging. The flocs are light, fluffy conglomerates which are held together by weak van der waals force of attraction. Aggregation is achieved by adding flocculating agents. For instance, by the addition of more anions on to a positively charged deflocculated particles flocculation’s can be achieved. This system possesses better physical stability characteristics, but its bioavailability is less when compared to deflocculated system, because the dissolution of flocs is a prerequisite for drug absorption.
- Deflocculated suspension— In this system, solid are present as individual particles. They also exhibit aggregation, but comparatively at a slower rate than the flocculated particles. These systems have a shorter shelf life, but have greater bioavailability when compared to flocculated systems.
Common Preparation method of Suspension.
Small scale preparation is done into the many steps—
- Suspension is prepared by grinding or levigating the insoluble material in the mortar to a smooth paste with a vehicle containing the wetting agent.
- All soluble ingredients are dissolved along with some portion vehicle and added with the previous solution to get the slurry.
- The slurry is transferred to a graduated cylinder, the mortar is rinsed with successive portion of the vehicle.
- Decide whether the solids are-
- Suspended in a structured vehicle or
- Flocculated or
- Flocculated and the suspended.
- Finally add the vehicle containing the suspending agent or flocculating agent and make up the dispersion to the final volume.
NOTE— Large scale preparation having the same steps but these steps are carried out using sophisticated equipment’s such as dough mixer, pony mixer etc.
Formulation of the suspension
Formulation of a suspension depends on whether the desired suspension is flocculated or deflocculated.
- On approach involves the use of structured vehicles to keep particles in a deflocculated state.
- The second approach keep particles in a flocculated state in order to prevent the cake formation.
- Third method uses a combination of earlier approaches to prevent settling.
Dry Powder for Reconstitution
You will frequently have the opportunity to reconstitute or compound
drugs that are in a dry powder form. These are usually drugs such as
antibiotics, which lose their potency in a short period of time after being
prepared in a liquid dosage form.
- Establish how much of a drug is contained in a vial or bottle.
- Calculate the powder volume displacement of a reconstituted drug.
- Solve problems related to dry powders.
D.Pharma Notes
B.Pharma Notes
- B.Pharma First Year
- B.Pharma Second Year
- B.Pharma Third year
- B.Pharma Fourth Year
