Communicable Diseases
What is Communicable disease:-
A disease in which the causative organism may pass or carried from person to person directly or indirectly.
Example:- Cholera, Typhoid, Leprosy, Tuberculosis, etc.
Transmissions of Communicable disease:-
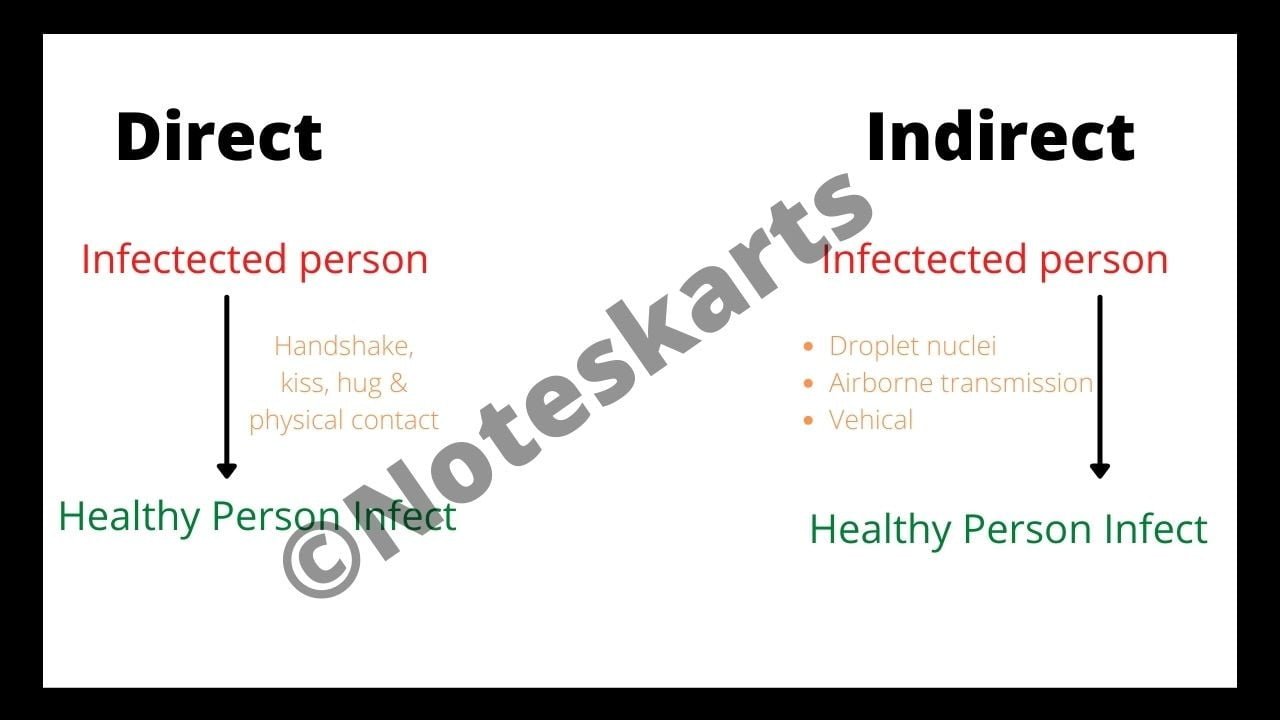
1. Direct:- In this case, by coming in direct contact with the infected person, the healthy person becomes a victim of infection. Direct contact such as handshake, kiss, hug, physical contact etc.
2. Indirect:- In this case, he influences the person indirectly like spreads through airdrops, chicks etc.
1. Respiratory infections :
| Diseases Name | Causative Agents | Mode of transmission | Prevention | |
| 1. | Chicken Pox | Varicella-Zoster (V-Z) | · Transmitted by droplet infection · Transmitted by personal contact · It can also cross the placental barrier and infect the foetus. | Notification, Isolation for 6 days after the onset of rash. Varicella Zoster Immunoglobulin can be given within 72 hours of ecposure. |
| 2. | Measles | The causative agent is RNA paramyxo virus or Measles virus. OR Measles Virus | · Infective material is secretion of nose, throat and respiratory tract · Transmission by droplet infection and droplet Nuclei | Isolation of the potient for 7 days after the rash. Immunisation of contact with in 2 days of exposure. Prevention by measles vaccination. It is given at 9 month of age. |
| 3. | Diphtheria | · Corynebacterium diptherial · It is a gram positive rod shaped | · Transmitted mainly by the droplet infection, · Transmitted through Fomites is also passible | Prevention is by immunization with DPT. It must be given at 6th, 10th and 14th month of a child. A booster dose is given at 1 ½ year at 5 years DT is given. |
| 4. | Influenza. | · Influenza virus | · Transmitted by droplet · Infection or Droplet nuclei. | Influnza can be Prevented by the administration of Vaccines. The Prophylactic drug is amantadine. |
| Diseases Name | Causative Agents | Mode of transmission | Prevention | |
| 5. | Tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | · Transmitted by droplet infection & droplet nuclei · It is also transmitted by fomites. · Elies which transmit theinfect by contaminating food. · Poverty, overcrowding and poor ventilation. | Chemoprophylaxis Give the suitable drugs such as INH, rifampicin and streptomycin. Immunisation by BCG vaccination. |
| 6. | Whooping Cough | Bordetella Pertussis. | · Transmitted by the infected patient · Disease is spreads by droplet infection and through fomites. | Isolation of contact and cases. Treatment with erythromycin. Active immunization with pertussis vaccine or DPT vaccine. |
2. Intestinal Infections :-
| Diseases Name | Causative Agents | Mode of transmission | Prevention | |
| 1. | Poliomyelitis | Polio virus Type-1 Type-2 Type-3 | · Transmitted by infected person. · Transmission by fecal-oral route. · Direct infection by contaminated fingers | · Notification and isolation of the patient. · Proper disposal of urine and faces avoidance of overcrowding in school and in public gatherings. · Immunisation with salk vaccine and sabine vaccine. |
| 2. | Cholera | Vibrio cholera | · Fecal contamination of water. · Direct contact through contaminated fingers while handling excreta and fomites. | · Isolation and notification · Treatment by antibiotic like tetracycline. · Prevention by cholera vaccine, especially during fairs and festivals. |
| 3. | Typhoid Fever | Solmonellatyphi | · Transmitted by contaminated water and food. · Also transmitted by fingers & flies. · Transmitted by Feces and urine. | · Notification to health authorities. · Sanitary measures like safe · Detection of carriers and treating them · Immunisation with TAB vaccine. |
| 4. | Hepatitis Hepatitis-A
Hepatitis-B | Hepatitis-A virus
Hepatitis-B virus | · It is transmitted through contaminated water food and milk. · Homosexuallty is also cause for transmission.
· Transmitted through contaminated syringes and needles, transfusion,tattooing etc. · Also transmitted through placenta and through sexual contact. | · Safe disposal of excreta. · Prevention of contamination of water, food and mill. · Passive immunization with human normal immunoglobulin.
|

Vary nice notes..thank you so much sir but our exam coming on 26th May so give me all notes social pharmacy chapter 4….
Diploma 1st year notes given imidatly