Topical Preparations Pharmaceutics-2023-24
Table of Contents
Topical preparations.
Introduction—Colloids, liniment, lotions, paints, and some, solution are the preparation applied topically to the skin, douches, ear drops, enemas, irrigations, nasal drops, sprays and other solution alternatively are the preparation instilled into body cavities.
- The container and closures used for this preparation should be different from those used for oral preparations, should be different from those used for oral preparations, colour is the only distinguishing feature between bottle and ribbed oval used for mouthwashes.
- The inhalation preparations to be inhaled or sprayed should be packed in colourless fluted bottles, because the drug is delivered to the respiratory tract.
Ointments
Definition— Ointment is defined as a semisolid preparation intended for external application to the skin or mucous membranes. The components of an ointments often do not melt upon application to the skin. They are used topically on a variety of body surface. These include the skin and the mucous membranes of the eye (eye ointment), vagina, anus and nose. Ointments may or may not be medicated.
Advantages.
- They are easy to handle than the bulky liquid dosage forms.
- They are directly applied to the target area avoiding the other body parts.
- Patients sensitive to parenteral and oral route prefer ointment.
Disadvantages.
- They are bulkier than the solid dosage form.
- They required high cost of production.
- They may cause skin irritation.
- They may get contaminated when applied using fingers.
Classification of ointment.
- Medicated ointment— Ointments which shows the therapeutics effects.
- Non medicated ointment—This may be used as a protector, emollient, lubricant or may be used as a vehicle for topical application of therapeutic agent.
Ointment bases
- Hydrocarbon bases (oleaginous bases)— Hydrocarbon base shows the emollient effect on the skin and protect the dryness of the skin. Immiscible with water and difficult to washing, they can remain on skin for longer time without drying out. They usually consist of soft paraffin or mixtures of soft paraffin with hard paraffin or liquid paraffin.
- Absorption bases—It is two types.
- Non-emulsified—These bases absorb water to form water-in-oil emulsions. Generally, they consist of a hydrocarbon base combined with a water-in-oil emulsifier. Example-wool fat, wool alcohol, beeswax and cholesterol.
- W/O emulsions— These are similar to non-emulsified bases but are capable of absorbing more water. Example- lanolin (hydrous wool fat), oily cream.
- Water removal bases/emulsifying bases— These are oil in water emulsions having an emulsifier which makes them readily miscible with water. They may be diluted with water or aqueous solution. Example- hydrophilic ointment, vanishing cream.
- Water soluble bases/Greaseless bases— These have been developed from polyethylene glycols (macrogols). They are non-occlusive, mix readily with skin secretions and are easily removed by washing. They mostly used for incorporation of solid substances. Example-PEG ointment.
Criteria for selection of ointment bases.
- Desired release rate of the drug substance from.
- Desirability for topical or percutaneous drug
- Desirability of occlusion of moisture from the
- Stability of the drug in the ointment base.
- Effect of the drug on the consistency or other
Preparation method of ointments.
- Incorporation method— By the incorporation, the components are mixed until a uniform preparation is attained. Two types-
- Incorporation of solids.
- The ointment base placed on one side of preparation area and the powdered components, previously reduced to fine powders and thoroughly blended in a mortar, on the other side.
- Then add some amount of ointment bases in the powder drug and spatulated the mixture.
- Further, remaining ointment bases are added and continue the spatulation until mixture are uniformly blended.
- Incorporation of liquids.
- Liquid substances are added to an ointment after consideration of an ointment bases capacity to accept the volume required.
- Small amount of an aqueous solution may be incorporated into an oleaginous ointment.
- Hydrophilic ointment bases readily accept aqueous solution. Addition of aqueous preparation to a hydrophobic base.
- First the aqueous solution incorporated into a small amount of a hydrophilic base.
- Second that mixture then added to a hydrophobic base.
- Fusion— This involves melting together the bases over a water bath before incorporating any other ingredients. The ointment base may include a mixture of waxes, fats and oils, of which some are solid at room temperature and others are liquid.
Creams
Definition— Pharmaceutical creams are semisolid preparations containing one or more medicinal agents dissolved in either an o/w or w/o emulsion. Oil in water creams is more comfortable and cosmetically accepted as they are less greasy and can be easily washed off by water.
Creams have a relatively soft, spreadable consistency. Basically, creams are meant for application onto the skin. It contains oil in large amounts, some of which are inedible, hence creams are not used for internal use it is major disadvantages of this formulation.
Classification of cream.
- O/W emulsified cream— Example-vanishing cream, shaving cream.
- W/O emulsified cream— Example- cold cream, emollient cream.
Cold cream— Cold cream shows the protective effects on the skin from the different environmental factors and also used as moisturizer, makeup remover and cleanser. The main principle of cold cream involves slow evaporation of water phase which leads to cooling sensation. Borax, beeswax is used as an emulsifying agent other ingredients like mineral oils (liquid paraffin), alcohol, glycerine, lanolin and perfuming agent.
Ideal characteristic of cold cream
- Should have optimum pH (4.6-6).
- Consistency should be optimum
- Should not be sticky
- Should be attractive in appearance
- Penetration through epidermis of skin should be desirable.
- Must be non-irritant and non-inflammatory.
- Should give cooling effects.
Vanishing cream— vanishing creams get their name from the fact that they seemed to disappear when spread onto the skin and produce emollient and moisturizing effects. Ingredients used as stearic acid, an alkali, glycerol water etc.
Ideal characteristic of vanishing cream.
- High melting point.
- Pure whiteness.
- Very little odour and low iodine number.
- Rubbed easily on the skin without roll-on effect.
Pastes.
Definition—Pastes are the semi solid preparations meant for external applications to the skin. They contain large amount of finely powdered solids like starch, zinc oxide etc. Due to presence of these substances, they have viscosity and stiffness and less attractive cosmetically. Since paste are stiff, they do not melt at ordinary temperature thus forming and holding a protective coating over the area they are applied.
- Differences between ointment and paste.
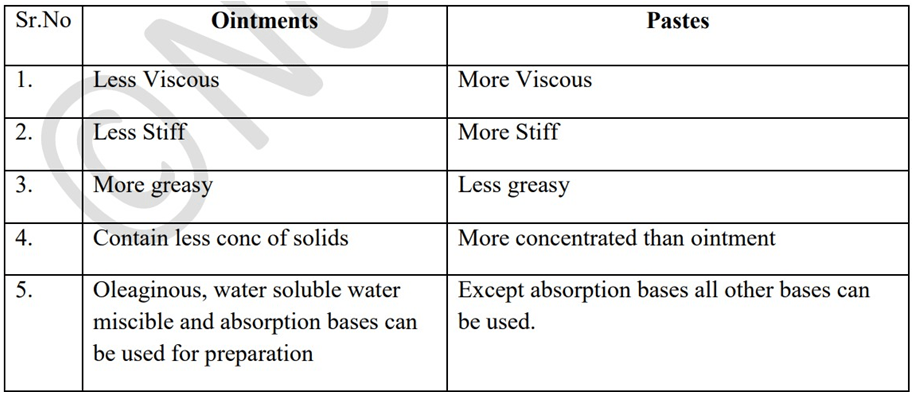
Gels.
Definition— Pharmaceutical gel is one of the semisolid preparations intended for the topical use on the skin and mucous membrane. Diclofenac gel are the analgesic gel preparation which are applied on the skin and other gel include as mouth ulcer gel which are applied in the oral cavity/mucosa.
The polymers used to prepare pharmaceutical gels include the natural gums tragacanth, pectin, carrageen, agar and alginic acid, synthetic and semisynthetic materials such as methylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose.
Classification of the gel.
- Based on the colloidal nature.
- Two phase/inorganic gel— Particle size of the dispersed phase is relatively large and forms the three-dimensional structure throughout the gel and it consists of floccules of small particles rather than larger molecule and gel structure. It is highly unstable.
- One phase/organic gel— it consists of large organic molecule existing on the twisted strands dissolved in the continuous phase. Organic gel either natural or synthetic and having the random motion of the organic molecule or bound together by the van der waal forces.
- Based on the solvent use.
- Hydrogels (aqueous solvent).
- Organogels (non-aqueous solvent).
Common preparation method of gel.
- Firstly, water soluble ingredients are dissolved in vehicle, in a mixing vessel by using mechanical stirrer.
- To prevent aggregation, add hydrophilic polymer to the stirred mixture slowly.
- Stirring is continued until the dissolution of the polymer has occurred.
- The mixing rate must not be extreme or a mixing vessel may be used to which a vacuum may be pulled to prevent the trapping of air.
NOTE— Gel is mainly prepared by the three methods- fusion method, cold method, and dispersion method.
Liniments
- Definition—They are defined as the liquid or semi solid preparations meant for application to the skin. They are applied to the skin with friction and rubbing of the skin due to rubbing nature it is also called as the embrocation. A liniment should not be applied to broken skin because it may cause excessive irritation. The vehicle should be selected for the type of action desired (rubefacient, counterirritant, massage) and also on the solubility of the desired components in the various solvents.
Classification of liniments.
- Alcoholic liniments— Due to the alcoholic solvent it having the more penetrating power in the skin, so it is mostly used for the local therapeutic preparation.
- Oleaginous liniments—Milder in their action but is more useful when massage is required.
Lotions
Definition—Lotions are defined as the liquid suspensions or dispersions meant for external applications to the skin without friction. Most lotions are o/w emulsions. They usually contain alcohol and glycerine because alcohol fasten drying and produces cooling sensation whereas glycerine keeps the skin moist for a sufficient long time.
A wide variety of other ingredients such as fragrances, glycerol, petroleum jelly, dyes, preservatives, and stabilizing agents are commonly added to lotions for improved organoleptic and preservation characteristics.
Lotions can be used for the topical delivery of medications such as antibiotics, antiseptics, antifungals, corticosteroids, antiacne agents, and soothing/protective agents (such as calamine).
Types of lotions—
- Cleansing lotion.
- Calamine lotion.
- Skin moisturizing lotion.
- Body lotion etc.
Suppositories
Definition— Suppositories is the solid/semisolid dosages form generally inserted into body cavity like rectum, vagina, urethra, nasal cavity, ear cavity (other than oral cavity) where they melt or soften at body temperature and release the drugs and shows their local and systemic action.
Whereas vaginal suppositories some time called as pessaries are also made as compressed table that disintegrate in body fluid. Suppository available in different sizes and shape.
Advantages
- Drugs are rapidly absorbed in rectal mucosa without ionisation.
- Drugs sensitive to acidic pH can be administered safely.
- Non – Sedating and bitter drugs can be given in this form without difficulties.
- These can easily administer to children old person and to unconscious patient, who cannot be swallow the drug easily.
- These are inserted into rectum to promote evaluation of the bowl.
- It is suitable for the drugs which are destroyed by portal circulation.
Disadvantages
- The irritating drug can’t be administered by this route.
- Absorption of drug through rectum is irregular.
- The most important problem is storage condition because it stored at low temperature (10-20 0 C). Other than the bases get liquefied.
- These is leaking problem of material through cavity thus found uncomfortable.
Types of suppositories.
- Rectal suppository.
- Vaginal suppository.
- Urethral suppository.
- Nasal suppository.
- Ear suppository/cone.
Formulation of suppositories.
- Hydrophilic bases. Example- Polyoxyethelene stearates, Sorbitan fatty acid esters, glycero-gelatine, poly ethylene glycol.
- Lipophilic/oleaginous bases. Example-Coca butter,
- Miscellaneous bases (combination of both).
- Antioxidants, hardening gents, preservatives, plasticizers (tween 80/85).
Preparation method of suppositories— Based on the molding it is prepare by-
- Hand molding.
- Automatics Machine Molding (rotatory machine, linear machine).
- Compression Molding.
- Heat Molding.
Pessaries.
Definition—They are solid dosage form of medicament meant for introduction into vagina. They either melt or dissolve in cavity fluids to release a medicament and exert a local action.
Example: lactic acid, ampicillin, nystatin, etc.
Nasal preparations
Definition—Nasal preparations are usually solutions or suspensions administered by the nose to treat nasal symptoms. They include medicines such as nasal steroids, lubricants, antihistamines and decongestants and anti-infectives, used to treat hay fever symptoms, congestion and infections.
Types of nasal preparation.
- Nasal spray— Medicated saline nasal preparation is done into the spray form which are administered, by applying the pressure on container which treats the nasal congestion and nasal rhinitis. Example-Oxymetazoline HCl nasal spray, fluticasone furoate nasal spray etc.
- Nasal drop/solution— They are aqueous solutions or liquid paraffin solutions meant for instillation into the nostrils by means of dropper. They are commonly used for their antiseptic, local analgesic or vasoconstrictor properties. Examples– Ephedrine nasal drops, xylometazoline nasal drop.
Formulation of nasal preparation
- Nasal spray formulations may be water-based, hydroalcoholic, nonaqueous, suspensions, or emulsions.
- A formulation can include diverse excipients, including solvents, mucoadhesive agents, buffers, antioxidants, preservatives, and penetration enhancers (i.e., compounds to improve absorption or penetration).
Ear preparations
Definition— Ear/aural preparation are liquid preparations in which drug are dissolved or suspended in suitable vehicle like water, dilute alcohol, glycerine and are instilled into ear with a dropper. They are generally used for clearing ear, softening the wax and for treating infections.
Types of the ear preparation.
- Ear drop/solution— External part of ear consists of the auditory canal which is formed by the skin and cartilage. Ear preparation direct instilled into the cavity which prevents the microbial infection, fungal infections etc. Ear preparation also used as the analgesic, wax softeners, anti-inflammatory.
- Example— Hydrogen peroxide ear drops, ofloxacin otic solution, Clotrimazole 1% solution, benzocaine turpentine ear drops etc.
D.Pharma Notes
B.Pharma Notes
- B.Pharma First Year
- B.Pharma Second Year
- B.Pharma Third year
- B.Pharma Fourth Year


